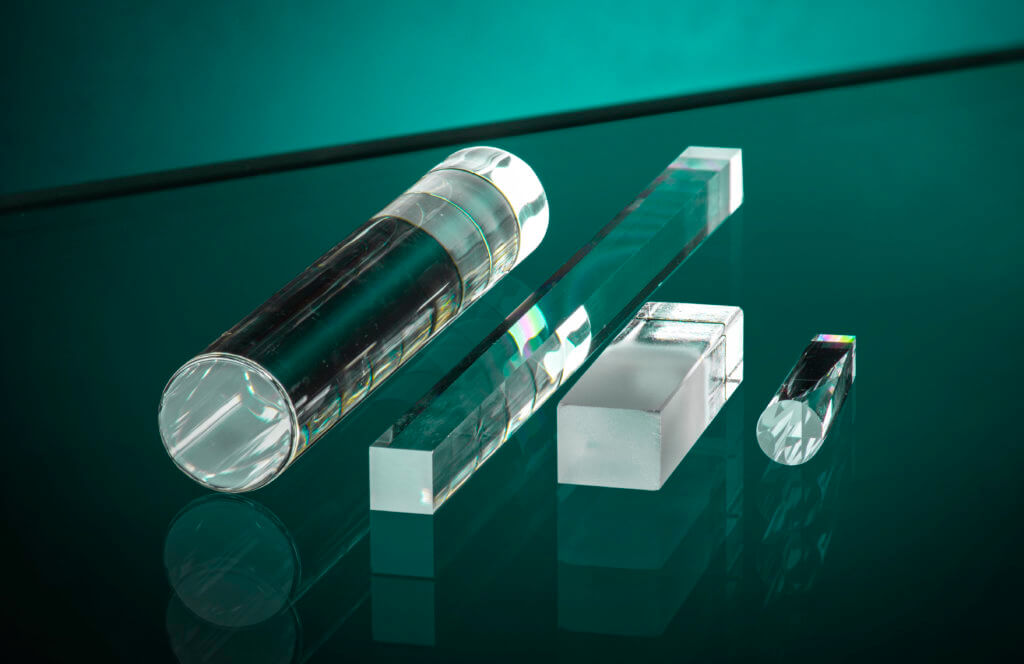
Fused quartz is a highly versatile material with exceptional properties and caters to a wide variety of industrial and scientific needs. Its unique composition offers a range of benefits that meet demanding requirements.
Renowned for its exceptionally low coefficient of thermal expansion, fused quartz boasts unparalleled resilience against temperature fluctuations, making it indispensable in environments subjected to extreme heat or cold. This characteristic, combined with its remarkable material strength and resistance to chemical corrosion, makes fused quartz an optimal choice for enduring harsh conditions, particularly in acidic settings.
The optical clarity of fused quartz, owing to its smooth surface, enhances visibility and precision in scientific and industrial applications, facilitating accurate observations and analyses. Additionally, its resistance to abrasion and scratches ensures longevity and reliability in diverse operational settings.
With a wide temperature tolerance encompassing both high heat and extreme cold, fused quartz finds extensive utility in chemical and pharmaceutical processes, as well as in cryogenic applications. Its ruggedness and technical superiority, coupled with cost-effectiveness, position it as a favored and economical alternative to materials offering similar properties.
This inert and nonflammable material finds broad use across a spectrum of industries, including but not limited to optical components, lighting technology, laboratory equipment, pharmaceutical tubing, and analytical instruments. Its versatility and reliability make fused quartz an indispensable asset in modern engineering and scientific endeavors, embodying the pinnacle of material innovation.
Characteristics of Fused Quartz:
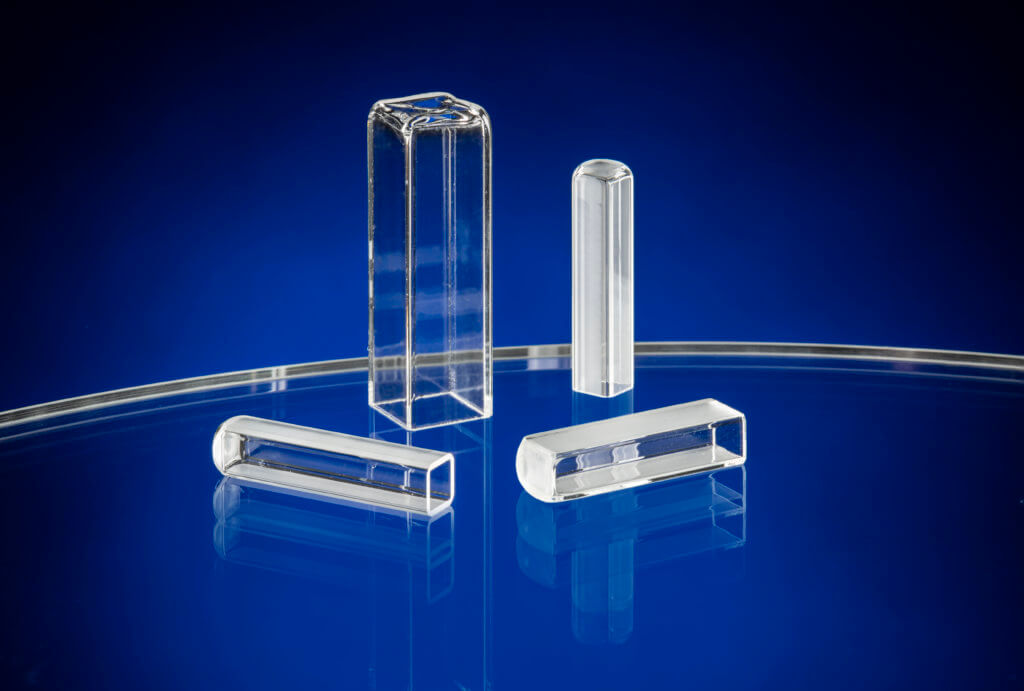 High Purity: Fused quartz exhibits exceptional purity, with minimal impurities that could interfere with optical transmission or semiconductor processes.
High Purity: Fused quartz exhibits exceptional purity, with minimal impurities that could interfere with optical transmission or semiconductor processes.- Optical Transparency: With 90% transmittance down to 260nm, it demonstrates excellent transparency across a broad spectrum from ultraviolet to infrared wavelengths, enabling applications in optics and photonics.
- Thermal Stability: It’s low coefficient of thermal expansion at (0/300°C): 5.5X10 -7/°C , ability to withstand working temperatures of more than 1,000°C., and high resistance to thermal shock ensure dimensional stability and reliability under extreme temperature variations.
- Chemical Inertness: Resistant to most acids, bases, and other corrosive chemicals, making it suitable for applications involving exposure to harsh environments.
- Mechanical Strength: Although brittle, fused quartz possesses sufficient mechanical strength with a tensile strength in excess of 4.8 x 107 Pa (7,000 psi) that can withstand typical handling and operational stresses in most applications.
- Electrical Insulation: High electrical resistivity makes it an excellent insulator for electrical components and devices.
- Low Fluorescence: Minimal fluorescence under ultraviolet excitation, crucial for applications requiring precise optical detection and measurement.
Here are the top five industries and their respective applications where fused quartz plays a crucial role:
- Optics and Photonics: Fused quartz is extensively utilized in optics and photonics industries due to its high optical transparency across a wide spectrum, ranging from ultraviolet to infrared wavelengths. Applications include:
- Precision lenses and prisms for scientific instruments and high-resolution imaging systems.
- Optical windows and components for laser technology, spectroscopy, and microscopy.
- Ultraviolet (UV) filters and lenses for applications such as sterilization, water purification, and UV curing.
 Semiconductor Manufacturing: In semiconductor fabrication processes, where purity and precision are paramount, fused quartz is indispensable. Its key applications include:
Semiconductor Manufacturing: In semiconductor fabrication processes, where purity and precision are paramount, fused quartz is indispensable. Its key applications include:
- Substrates for semiconductor wafers, ensuring uniform heating and thermal stability during processing.
- Process tubes, wafer carriers, and crucibles in high-temperature furnaces for doping, oxidation, and deposition processes.
- Quartz glassware for chemical handling and containment in cleanroom environments, maintaining high levels of cleanliness and chemical resistance.
- Aerospace and Defense: Fused quartz plays a critical role in aerospace and defense applications where reliability under extreme conditions is essential. Key applications include:
- Rocket nozzles and combustion chambers requiring high-temperature resistance and dimensional stability.
- Infrared (IR) windows and lenses for missile guidance systems and surveillance equipment.
- Protective covers for sensors and optical components in satellites and spacecraft, ensuring durability and optical clarity in harsh environments.
- High-Temperature Processes: Industries involved in high-temperature processes benefit from fused quartz’s ability to withstand extreme temperatures without softening or deforming. Applications include:
- Crucibles and containers for melting and processing high-purity metals and alloys in metallurgical applications.
- Thermocouple protection sheaths for accurate temperature measurement in industrial furnaces and kilns.
- Heating elements and lamps for industrial processes requiring controlled and uniform heat distribution, such as semiconductor annealing and glass manufacturing.
- Research and Laboratory Equipment: Fused quartz finds widespread use in research laboratories and scientific institutions due to its optical properties, chemical inertness, and thermal stability. Applications include:
- Quartz cuvettes for spectrophotometry and chemical analysis, providing optical clarity and chemical resistance.
- Evaporation boats and crucibles for material deposition in thin-film coating processes.
- Quartz glassware such as test tubes, beakers, and reaction vessels for handling corrosive chemicals and high-temperature reactions.